C#/ASP.NET/ASP MVC - Retrieve email using Gmail/G Suite OAuth 2.0 + IMAP4 protocol in background service (service account)¶
By default, you need to enable ” Allowing less secure apps” in Gmail/G Suite, then you can retrieve email with user/password IMAP4 authentication.
However Google will disable traditional user authentication in the future, switching to Google OAuth is strongly recommended now.
Sections:
- Installation
- Add reference
- .NET assembly
- Google Service Account
- Create project in Google Developers Console
- Create service account in current project
- Create service key
- Enable Gmail API
- Authorize service account by G Suite administrator
- Enable TLS Strong Encryption Algorithms in .NET 2.0 and .NET 4.0
- Access token lifetime
- C#/ASP.NET/ASP MVC - Retrieve email using Gmail/G Suite OAuth 2.0 from IMAP4 server with service account - example
- EA Oauth Service for Gmail
- TLS 1.2 protocol
- Related links
Installation¶
Before you can use the following sample codes, you should download the EAGetMail Installer and install it on your machine at first. Full sample projects are included in this installer.
Install from NuGet
You can also install the run-time assembly by NuGet. Run the following command in the NuGet Package Manager Console:
Install-Package EAGetMail
Note
If you install it by NuGet, no sample projects are installed, only .NET assembly is installed. And you also need to get a trial license code from here instead of using “TryIt”.
Add reference¶
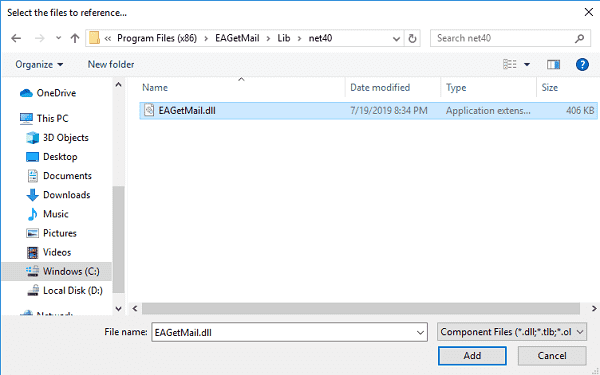
To use EAGetMail POP3 & IMAP Component in your project, the first step is “Add reference
of EAGetMail to your project”. Please create or open your project with Visual Studio,
then go to menu -> Project -> Add Reference -> .NET -> Browse..., and
select Installation path\Lib\[netversion]\EAGetMail.dll, click Open-> OK, the reference
will be added to the project, you can start to use it to
retrieve email and parse email in your project.
.NET assembly¶
Because EAGetMail has separate builds for .Net Framework, please refer to the following table and choose the correct dll.
Separate builds of run-time assembly for .Net Framework 2.0, 4.0, 4.5, 4.6.1, 4.7.2, 4.8.1, .NET 6.0, NET 7.0, .NET 8.0, .NET Standard 2.0 and .Net Compact Framework 2.0, 3.5.
| File | .NET Framework Version |
| Lib\[net20|40|45|461|472|481]\EAGetMail.dll |
Built with .NET Framework 2.0, 4.0, 4.5, 4.6.1, 4.7.2, 4.8.1
It requires .NET Framework 2.0, 3.5 or later version. |
| Lib\[net6.0|7.0|8.0]\EAGetMail.dll |
Built with .NET 6.0, .NET 7.0, .NET 8.0
It requires .NET 6.0 or later version. |
| Lib\netstandard2.0\EAGetMail.dll |
Built with .NET Standard 2.0
It requires .NET Standard 2.0 or later version. |
| Lib\[net20-cf|net35-cf]\EAGetMail.dll |
Built with .NET Compact Framework 2.0, 3.5
It requires .NET Compact Framework 2.0, 3.5 or later version. |
Google Service Account¶
Normal OAuth requires user input user/password in Web Browser. Obviously, it is not suitable for background service. In this case, you should use google service account to access G Suite or Google Workspace email service without user interaction. Service account only works for G Suite or Google Workspace user, it doesn’t work for personal Gmail account.
Create project in Google Developers Console¶
To use “G Suite or Google Workspace Service Account OAuth” in your application, you should create a project in Google Cloud Console at first.
Important
You can use any google user to create service account, it doesn’t require service account owner is a user in G Suite. But G Suite or Google Workspace administrator must authorize service account in Google Admin Console to access user mailbox.
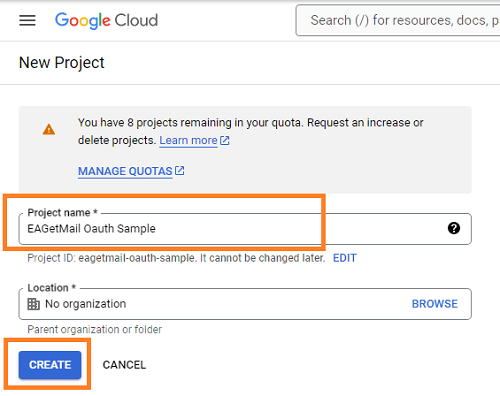
Open Google Cloud console, create a new project by https://console.cloud.google.com/projectcreate.
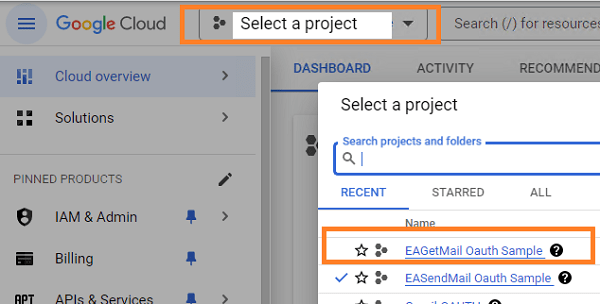
After the project is created, select it from projects list as current project.
Create service account in current project¶
Click
"Credentials"->"Manage service accounts"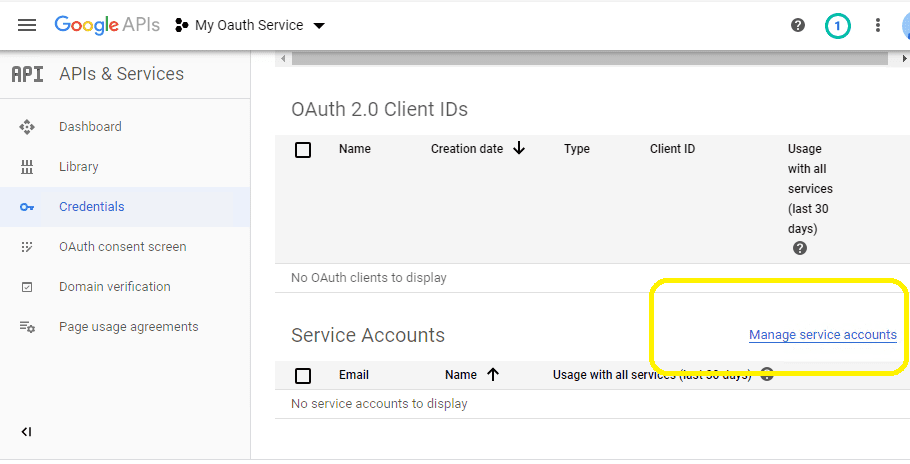
Click
"CREATE SERVICE ACCOUNT"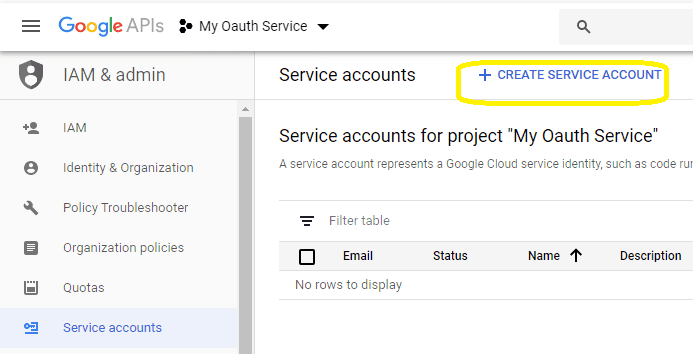
Input a name for your service account, click
"DONE"
After service account is created, you should enable "Domain-wide delegation" and create service key pair
to access G Suite or Google Workspace user mailbox.
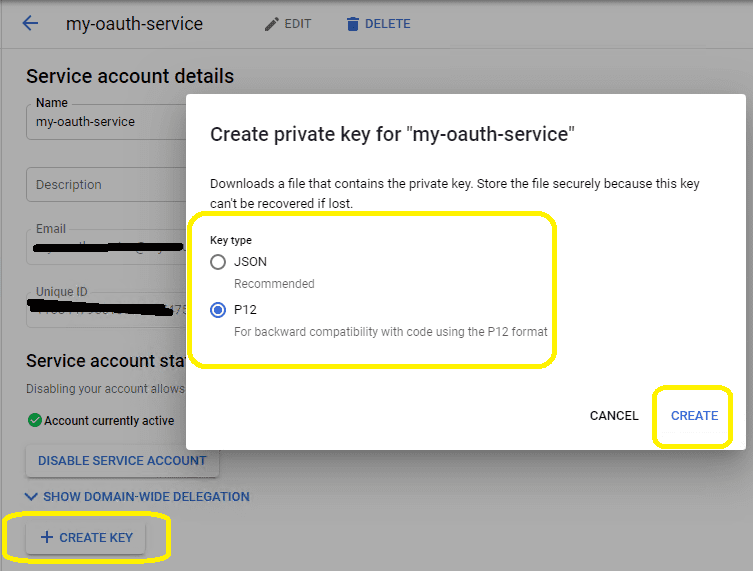
Create service key¶
Go back to your service account -> Keys, click
Add Key, you can select"p12"or"json"key type, both can work well, then you will get a file which contains private key, save the file to local disk.Now you have created service account with key pair successfully. You can use created private key in your codes to request
"access token"impersonating a user in G Suite or Google Workspace.
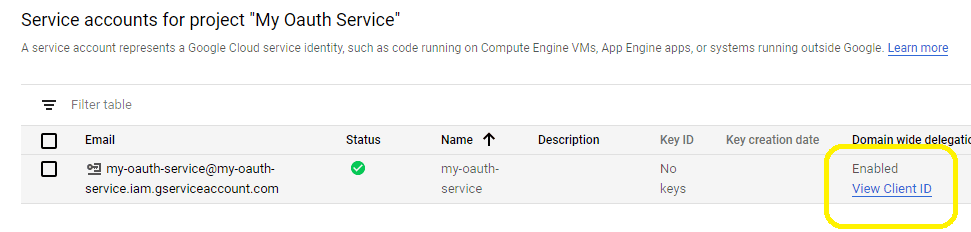
- To access user data in G Suite, you must get authorization from G Suite or Google Workspace administrator. You should go back to your service account -> Details, copy your service account email address and client id.
Enable Gmail API¶
Enable Gmail API in "Library" -> Search "Gmail", then click "Gmail API" and enable it.
Authorize service account by G Suite administrator¶
To use service account to access user mailbox in G Suite or Google Workspace, G Suite Administrator should authorize specified service account at first.
Important
Important Notice: You can use any google user to create service account, it doesn’t require service account owner is a user in G Suite or Google Workspace. But G Suite or Google Workspace administrator must authorize service account in G Suite or Google Workspace Admin Console to access user mailbox.
The administrator should open admin.google.com, go to Admin Console, click
"Security">API Control;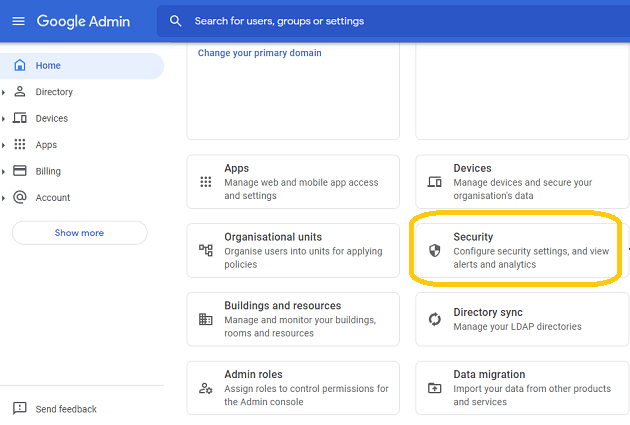
In the Domain wide delegation pane, select Manage Domain Wide Delegation.
Click Add new.
In the Client ID field, enter the service account’s Client ID
Click Add new and enter your service account client ID.
Enter the
client IDof the service account or OAuth2 client ID of the app.In the OAuth scopes (comma-delimited) field, enter the list of scopes that your application should be granted access to. and input
https://mail.google.com/,email,profilein One or More API Scopes, click"Authorize".
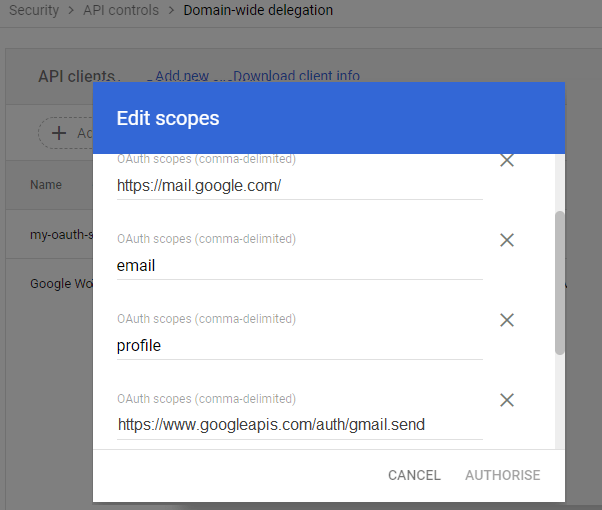
- Click Authorize.
After the administrator authorized service account, you can use it to access any users mailbox in G Suite or Google Workspace domain.
Learn more detail from: https://developers.google.com/identity/protocols/oauth2/service-account
Enable TLS Strong Encryption Algorithms in .NET 2.0 and .NET 4.0¶
Because HttpWebRequest is used to get access token from web service.
If you’re using legacy .NET framework (.NET 2.0 - .NET 3.5 and .NET 4.0 - 4.6.1),
you need to enable Strong Encryption Algorithms to request access token:
Put the following content to a file named NetStrongEncrypt.reg, right-click this file -> Merge -> Yes.
You can also download it from https://www.emailarchitect.net/webapp/download/NetStrongEncrypt.zip.
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\.NETFramework\v2.0.50727]
"SystemDefaultTlsVersions"=dword:00000001
"SchUseStrongCrypto"=dword:00000001
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\Microsoft\.NETFramework\v2.0.50727]
"SystemDefaultTlsVersions"=dword:00000001
"SchUseStrongCrypto"=dword:00000001
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\.NETFramework\v4.0.30319]
"SystemDefaultTlsVersions"=dword:00000001
"SchUseStrongCrypto"=dword:00000001
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\Microsoft\.NETFramework\v4.0.30319]
"SystemDefaultTlsVersions"=dword:00000001
"SchUseStrongCrypto"=dword:00000001
Access token lifetime¶
You don’t have to request access token every time. By default,
access token expiration time is 3600 seconds, you can reuse the access token repeatedly before it is expired.
C#/ASP.NET/ASP MVC - Retrieve email using Gmail/G Suite OAuth 2.0 from IMAP4 server with service account - example¶
// You can install Google.Apis.Auth.OAuth2 by NuGet
// Install-Package Google.Apis.Auth
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.Net;
using System.Net.Sockets;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Security.Cryptography.X509Certificates;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
using Google.Apis.Auth.OAuth2;
using EAGetMail;
using System.Globalization;
// Generate an unqiue email file name based on date time
static string _generateFileName(int sequence)
{
DateTime currentDateTime = DateTime.Now;
return string.Format("{0}-{1:000}-{2:000}.eml",
currentDateTime.ToString("yyyyMMddHHmmss", new CultureInfo("en-US")),
currentDateTime.Millisecond,
sequence);
}
public static void RetrieveMailWithGSuiteUser()
{
try
{
// service account email address
const string serviceAccount = "xxxxxx@xxxxx.iam.gserviceaccount.com";
// import service account key p12 certificate.
var certificate = new X509Certificate2("D:\\MyData\\myoauth-77dec4d192ec.p12",
"notasecret", X509KeyStorageFlags.Exportable);
// G Suite user email address
var gsuiteUser = "user@gsuitdomain.com";
var serviceAccountCredentialInitializer = new ServiceAccountCredential.Initializer(serviceAccount)
{
User = gsuiteUser,
Scopes = new[] { "https://mail.google.com/" }
}.FromCertificate(certificate);
// if service account key is in json format, copy the private key from json file:
// "private_key": "-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY-----\n...\n-----END PRIVATE KEY-----\n"
// and import it like this:
// string privateKey = "-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY-----\nMIIEv...revdd\n-----END PRIVATE KEY-----\n";
// var serviceAccountCredentialInitializer = new ServiceAccountCredential.Initializer(serviceAccount)
//{
// User = gsuiteUser,
// Scopes = new[] { "https://mail.google.com/" }
// }.FromPrivateKey(privateKey);
// request access token
var credential = new ServiceAccountCredential(serviceAccountCredentialInitializer);
if (!credential.RequestAccessTokenAsync(CancellationToken.None).Result)
throw new InvalidOperationException("Access token failed.");
// Create a folder named "inbox" under current directory
// to save the email retrieved.
string localInbox = string.Format("{0}\\inbox", Directory.GetCurrentDirectory());
// If the folder is not existed, create it.
if (!Directory.Exists(localInbox))
{
Directory.CreateDirectory(localInbox);
}
MailServer oServer = new MailServer("imap.gmail.com",
gsuiteUser,
credential.Token.AccessToken, // use access token as password
ServerProtocol.Imap4);
// Set IMAP OAUTH 2.0
oServer.AuthType = ServerAuthType.AuthXOAUTH2;
// Enable SSL/TLS connection, most modern email server require SSL/TLS by default
oServer.SSLConnection = true;
// Set IMAP4 SSL Port
oServer.Port = 993;
// Since EAGetMail 5.3.5, Gmail Rest API is supported as well. You can use the following code
// to retrieve email using Gmail Rest API.
// MailServer oServer = new MailServer("gmail.googleapis.com",
// userEmail,
// accessToken, // use access token as password
// ServerProtocol.GmailRestApi);
// oServer.AuthType = ServerAuthType.AuthXOAUTH2;
// oServer.SSLConnection = true;
MailClient oClient = new MailClient("TryIt");
// Get new email only, if you want to get all emails, please remove this line
oClient.GetMailInfosParam.GetMailInfosOptions = GetMailInfosOptionType.NewOnly;
Console.WriteLine("Connecting {0} ...", oServer.Server);
oClient.Connect(oServer);
MailInfo[] infos = oClient.GetMailInfos();
Console.WriteLine("Total {0} email(s)\r\n", infos.Length);
for (int i = 0; i < infos.Length; i++)
{
MailInfo info = infos[i];
Console.WriteLine("Index: {0}; Size: {1}; UIDL: {2}",
info.Index, info.Size, info.UIDL);
// Receive email from email server
Mail oMail = oClient.GetMail(info);
Console.WriteLine("From: {0}", oMail.From.ToString());
Console.WriteLine("Subject: {0}\r\n", oMail.Subject);
// Generate an unqiue email file name based on date time.
string fileName = _generateFileName(i + 1);
string fullPath = string.Format("{0}\\{1}", localInbox, fileName);
// Save email to local disk
oMail.SaveAs(fullPath, true);
// Mark email as read to prevent retrieving this email again.
oClient.MarkAsRead(info, true);
// If you want to delete current email, please use Delete method instead of MarkAsRead
// oClient.Delete(info);
}
// Quit and expunge emails marked as deleted from server.
oClient.Quit();
Console.WriteLine("Completed!");
}
catch (Exception ep)
{
Console.WriteLine(ep.ToString());
}
}
EA Oauth Service for Gmail¶
If your code is too complex or out of maintenance, and you don’t want to change anything in your source codes, then you can have a try with EA Oauth Service for Gmail. It provides an easy way for the legacy email application that doesn’t support OAUTH 2.0 to send and retrieve email from Gmail without changing any codes. SMTP, POP, IMAP and SSL/TLS protocols are supported.
TLS 1.2 protocol¶
TLS is the successor of SSL, more and more SMTP servers require TLS 1.2 encryption now.
If your operating system is Windows XP/Vista/Windows 7/Windows 2003/2008/2008 R2/2012/2012 R2, you need to
enable TLS 1.2 protocol in your operating system like this:
Enable TLS 1.2 on Windows XP/Vista/7/10/Windows 2008/2008 R2/2012
Appendix
- Retrieve email and parse Email in C# - Tutorial
- EAGetMail POP3/IMAP4 Component SDK
- Using UIDLManager to mark email as read/downloaded
- Download only unread/new emails from IMAP or MS Exchange Server
- Search emails and filter emails on IMAP or MS Exchange Server
- Retrieve emails from specified folder in IMAP or MS Exchange Server
Comments
If you have any comments or questions about above example codes, please click here to add your comments.