Add digital signature (S/MIME + RSA-PSS + SHA256) to email in Exchange Server 2007/2010/2013/2016/2019 - Tutorial¶
Digital signature ensures authenticity and data integrity between the email sender and recipient. It gives the recipient an assurance that the sender is who he claims to be and the email content was not altered in transit.
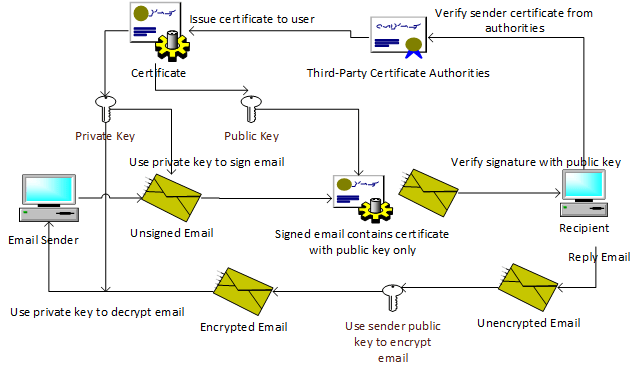
After an email was signed and arrived in the recipient’s email client, the email client will verify the email content with the sender’s public key and validate the certificate chain through trusted certification authorities. If the email content was changed or the certificate chain is invalid, the email client will warn the recipient.
Use digital signature (S/MIME) in email client¶
Most popular email clients support email digital signature. To setup digital signature in your email client, you need a digital certificate with a private key for the sender’s email address. You can refer to the documentation of your email client for the settings.
This tutorial introduces how to use S/MIME Plugin to add server-side digital signature to an email in Exchange Server automatically without an email client. If you send emails from an email tool that doesn’t support digital signature, this plugin can help to sign email on server side.
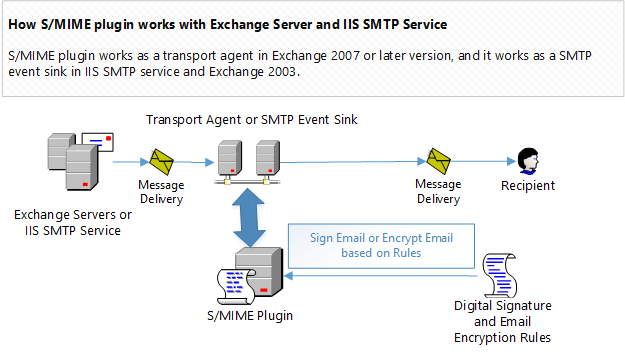
How S/MIME Plugin works?¶
In Exchange Server 2007/2010/2013/2016/2019, S/MIME Plugin works as a transport agent. It adds digital signature to an email based on pre-defined rules.
A digital signature rule can be defined for a single sender or multiple senders.
Install S/MIME Plugin in Exchange Server 2007/2010/2013/2016/2019¶
To enable S/MIME Plugin in Exchange 2007/2010/2013/2016/2019, download the EA Disclaimer and S/MIME Installer and install it on your server.
Note
Exchange Server Role
If you installed Exchange Server 2007/2010/2013/2016/2019 on multiple servers, you need to install this plugin on every Exchange Hub Transport Server Role.
Double click installer file and the installation will be executed automatically. Installer requires Exchange server to be installed. If no Exchange server detected in your operation system, Setup will be aborted.
After the installation is completed, click “Disclaimer and S/MIME Manager” from “Windows Start menu” -> “All Programs” -> “EA Disclaimer and SMIME for IIS and Exchange Server” to begin the setup.
Important
After the installation is completed, you must check “Microsoft Exchange Transport Service”
and “Microsoft Exchange Mail Submission Service” in Control Panel -> Administrative Tools -> Services,
if these services are not running, start them.
Import, export and generate test certificate¶
To view/import/export certificate in Current User Store and Local Machine Store, you can open the Certificates MMC Snap-in like this:
- On the
Windows Start menu, clickRun, and then typemmc. Click Enter. This starts the Microsoft Management Console (MMC). - In the console, click the
Filemenu and then clickAdd/Remove Snap-in.
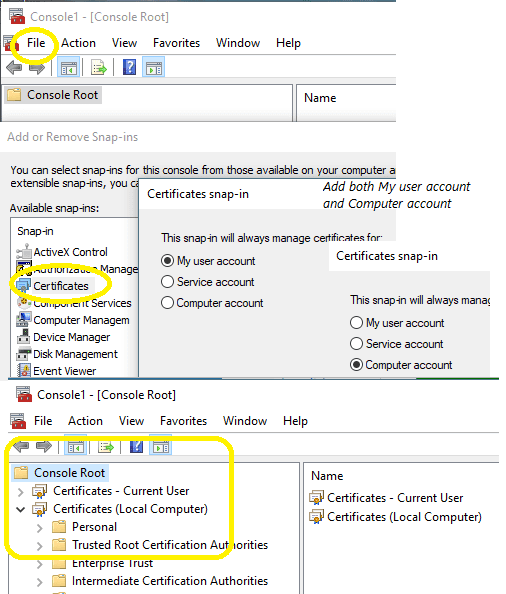
- In the
Add/Remove Snap-inwindow, click theAddbutton. - On the Snap-in list, select
Certificatesand then clickAdd. - In the Certificates Snap-in window, select
My user account, - and select
Certificatesand then clickAddagain. - In the Certificates Snap-in window, select
Computer account, and then clickNext. - In the Select Computer window, select
Local computer, and then clickFinish. This adds the Certificates Snap-in to the list. Close the window. - In the Add/Remove snap-in window, click
OK. This adds the Certificates snap-in to the mmc console. - Expand the Certificates node to see the different types of certificates.
Now you can view all certificates in current user store and local machine store.
As S/MIME Plug can’t access certificates from the Current User Store, if your certificate is stored in the Current User Store,
you must export it from the Current User Store.
Export certificate from certificate store¶
You can export certificate(s) from Current User Store like this:
Certificates MMC Snap-in, selectCertificates - Current User->Personal->Certificates,- Select the certificate(s) you want to export, you can select multiple certificates by
Ctrl+Left Click, - Right click ->
All Tasks->Export->Next - As signing email requires a private key, you need to select
Yes, export the private key,
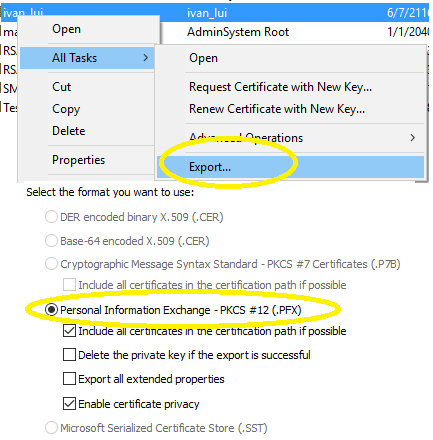
- Select
Personal Information Exchange - PKCS #12 (.PFX)->Next, - Check
Password, and input a password as protection password, - Save it as *.pfx file.
You can use exported pfx file as Certificate source in S/MIME Plugin.
Note
If you selected No, doesn't export private key, you can export the certificate as .cer, or pfx and sst (multiple certificate selected).
The certificate without a private key is used for email encryption only.
Pfx, Cert and Sst file¶
- Pfx file can contain multiple certificates with public/private keys, it can be used for both email signing and encryption.
- Cert file is a single certificate without a private key, it is used for email encryption only.
- Sst file contains multiple certificates without a private key, it is used for email encryption only.
Import certificate to certificate store¶
You can import a certificate file to Certificate Machine Store like this:
Certificates MMC Snap-in, selectCertificates - (Local Computer)->Personal->Certificates,- Right click ->
All Tasks->Import,
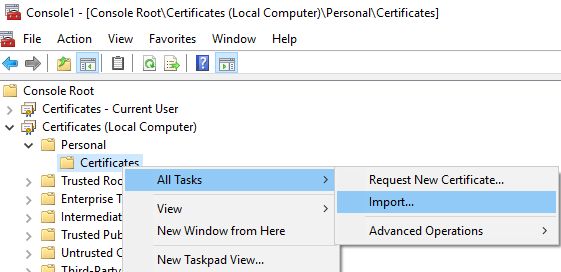
- Select certificate type and input certificate path ->
Next, - If it is pfx file, you should input pfx protection password and check
Mark this key as exportable ..., - Place all certificates in the following store:
Personal->Next->Finish.
After certificate file was imported to Certificate Machine Store, you can use Certificate Machine Store as Certificate source instead of certificate file.
Generate self-signed root certificate¶
If the email digital certificate is not issued by third-party authorities, the email client will prompt an error of “Certificate is not issued by a trusted publisher”.
However, for internal enterprise usage or test purpose,
you can create a self-signed root certificate and issue this digital certificate to internal users by New-SelfSignedCertificate PowerShell cmdlet.
Note
If you have an existing certificate from third-party authorities, you can skip this section.
Note
New-SelfSignedCertificate requires PowerShell 3.0 on Windows 10, Windows 8/8.1 and Windows Server 2012/2012 R2/2016.
You can create a root certificate like this:
New-SelfSignedCertificate -Type Custom -HashAlgorithm sha256 -KeyLength 2048 -KeyUsage CRLSign, CertSign, KeyAgreement, DataEncipherment, KeyEncipherment, DigitalSignature -KeyAlgorithm RSA -Subject "CN=Test Root V1" -CertStoreLocation "cert:\CurrentUser\My" -NotAfter (get-date).AddDays(7300)
Then the new root certificate can be found in Certificates MMC Snap-in, select Certificates - Current User -> Personal -> Certificates.
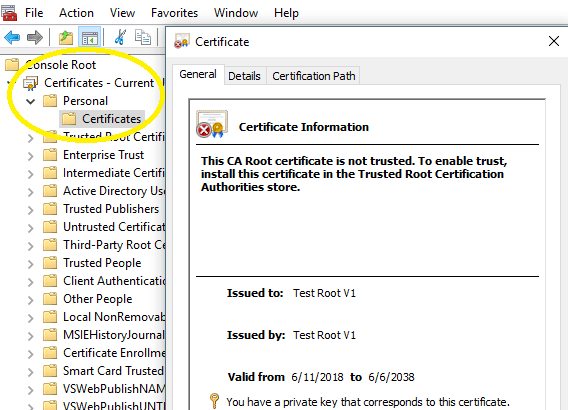
Now you can issue the certificate to users from root certificate like this:
Generate email certificate issued by root certificate¶
Here is an example to issue the certificate from the root certificate generated in the previous section.
Set-Location -path cert:\CurrentUser\My
$signer = Get-Childitem -DnsName "Test Root V1"
New-SelfSignedCertificate -HashAlgorithm sha256 -Type Custom -Subject "E=test@emailarchitect.net,CN=SMIME Tester 2048" -TextExtension @("2.5.29.37={text}1.3.6.1.5.5.7.3.4","2.5.29.17={text}email=test@emailarchitect.net&upn=test@emailarchitect.net") -KeyLength 2048 -KeyAlgorithm RSA -SmimeCapabilities -CertStoreLocation "Cert:\CurrentUser\My" -NotAfter (get-date).AddDays(365) -Signer $signer
Then the new email certificate can be found in Certificates MMC Snap-in, select Certificates - Current User -> Personal -> Certificates.
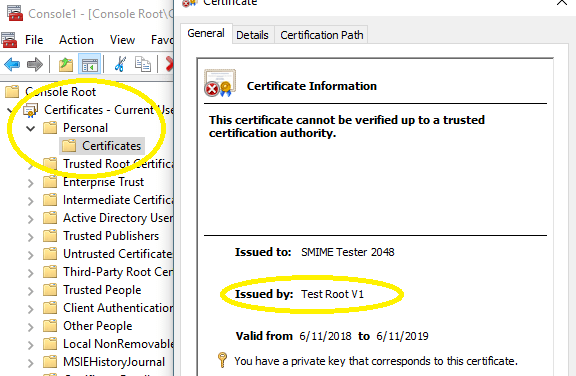
You can export it together with a private key as a pfx file and use it in Certificate source.
Alternatively, you can install a pfx file to Certificates (Local Computer) -> Personal -> Certificates and use Machine Store as Certificate Source.
Install root certificate to client machine¶
If you used the above certificate to sign emails, email client would give an error about Certificate is not issued by a trusted publisher.
You can install the root certificate to client machines like this to avoid the error.
Now you can export the root certificate to a cert file and install it on Trusted Root Certification Authorities:
Certificates MMC Snap-in, selectCertificates - Current User->Personal->Certificates,- Select the root certificate (Test Root V1),
- Right click ->
All Tasks->Export->Next - Select
No, do not export the private key,
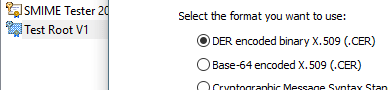
- Select
DER encoded binary X.509 (.CER), - Save it as .cer file.
Install it to Local\Computer\Trusted Root Certification Authorities
Certificates MMC Snap-in, selectCertificates - (Local Computer)->Trusted Root Certification Authorities->Certificates,- Right click ->
All Tasks->Import, - Select the .cer file from local disk ->
Next, - Place all certificates in the following store:
Trusted Root Certification Authorities->Next->Finish.
Install it to Current User\Trusted Root Certification Authorities
Certificates MMC Snap-in, selectCertificates - Current User->Trusted Root Certification Authorities->Certificates,- Right click ->
All Tasks->Import, - Select the .cer file from local disk ->
Next, - Place all certificates in the following store:
Trusted Root Certification Authorities->Next->Finish.
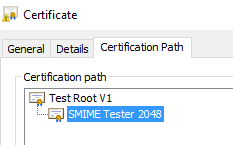
After you installed the root certificate to Trusted Root Certification Authorities, user certificate chain becomes valid now.
Create a rule for digital signature¶
You can create a test digital signature rule for a user like this:
- Click
Digital Signature->New, - Input any description for current rule,
- Input the user email address in
Sender Address,
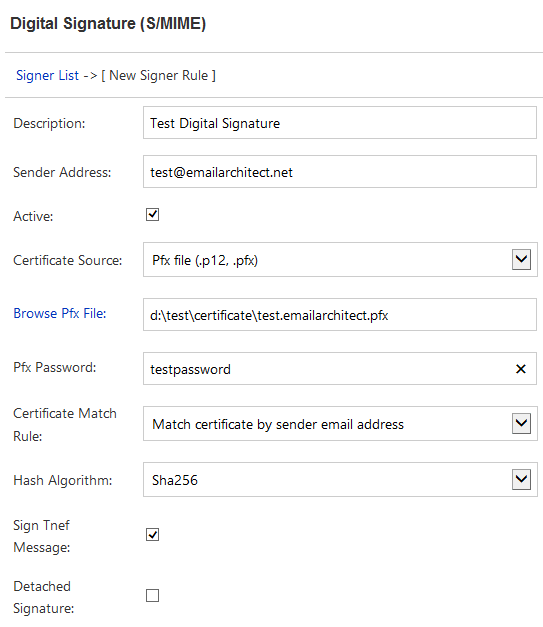
- Change
Certificate SourcetoPfx file (.p12, .pfx), - Input
Pfx file pathandPfx file password,
Important
IIS SMTP Service is running as Local System user, and Exchange Transport Agent is running as Network Service user,
so do not put the certificate file to Desktop or user-dependent folder,
S/MIME Plugin doesn’t have permission to read certificate files in these locations.
- Finally, click
Saveto save current rule.
After rule is saved, click Test, current rule will be executed with a virtual email message, you can find the result in test dialog box.
If Test all rules is checked, all rules defined on current machine will be executed with a virtual email message.
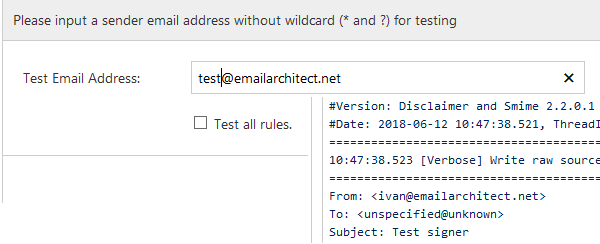
If the test result looks good, you can send a test email from that user, and validate if the received email was digital signed.
Certificate private key permission¶
Signing email requires certificate private key, if you got Access Denied error in Debug Log,
you can solve it like this:
If Certificate Source is pfx file, you can import it to Certificate Machine Store by Import Certificate to Certificate Store at first, then
change Certificate Source to Certificate Machine Store.
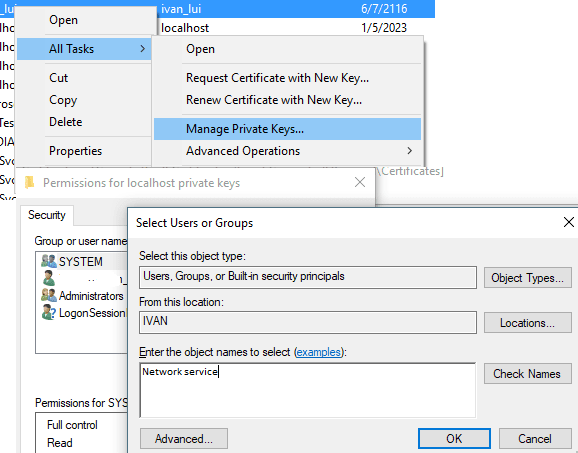
Now you can change the private key permission like this:
Certificates MMC Snap-in, selectCertificates (Local Computer)->Personal->Certificates,- Select the certificate you want to adjust the permission,
- Right click ->
All Tasks->Manage Private Key->Edit - Assign
Network Servicefull control to this key.
Sender address pattern and wildcard¶
A single email address or email address with wildcard (* and ?) can be used in Sender Address. It indicates current rule is only enabled for matched sender address.
A digital certificate can only be used for a specific email address. For example, you cannot use test@emailarchitect.net's certificate to
sign support@emailarchitect.net, email client would prompt an error due to address not match.
Therefore, if you used wildcard (* and ?) in sender address, you should specify a Certificate source that contains multiple certificates, and
set Certificate Match Rule to Match certificate by sender email address, to enable S/MIME Plugin to find the correct certificate to sign the email.
Note
If no certificate is identified for the current sender, the message won’t be signed.
Certificate source and certificate match rule¶
Certificate source¶
- Certificate Machine Store
- Look up the certificate from Windows built-in certificate machine store.
- Pfx File
- Look up the certificate from the specified P12/Pfx file.
Both machine store and pfx file can contain multiple certificates. Please refer to Import, Export and Generate Test Certificate to learn how to import/export certificate from the certificate store.
Certificate match rule¶
- Match certificate by sender email address
- This option is recommended. The digital certificate can be found based on sender email address, it can be used with any certificate source.
- Specified certificate
- To use this option,
Sender Addressmust not contain wildcard (* and ?). You can use it when the certificate subject doesn’t contain an email address.
Signature hash algorithm¶
Sha1, Sha256, Sha384 and Sha512 are supported. For security reason, you should use Sha256, Sha384 or Sha512 hash algorithm.
RSA-PSS padding in digital signature¶
To comply with EDIFACT in Germany/EUROPE, please check this option and use sha256 or higher SHA algorithm. If RSA-PSS padding in signature is used, because most email clients don’t support RSA-PSS signature verification, so they would report error for the digital signature. However it can be verified by EDIFACT authorities.
To use this feature, it also requires .NET framework 2.0, 4.0 or 4.61 installed on the server. Because .NET framework 2.0/4.0 is built-in feature in modern Windows Server, so you don’t have to install .NET framework manually in most cases.
Sign Tnef message¶
Tnef is an internal email format in Exchange Server. If this option is checked, Tnef messages will first be converted to RFC822/message format by S/MIME Plugin, and then be signed by the specified certificate.
Detached signature¶
If this option is checked, the signature is detached from email original data.
S/MIME Plugin troubleshooting¶
If your email was not signed as expected,
you should use Log Level to generate debug log like this:
Disclaimer and S/MIME Manager->Journal;- Select
Full Debug Logand clickChange Log Level; - Send a test email, debug log file will be available in
Installation path\logfolder very soon.
Important
Please be reminded to change the log level back to “Only Error Log” after troubleshooting, otherwise the log file size will be large.
If there is no log files in log folder, you can verify the Disclaimer Plugin installation.
Installation permission¶
When you install S/MIME Plugin on Exchange Server 2007/2010/2013/2016/2019, please make sure you are using “Domain Administrator” to run the installer.
Verify Exchange Transport Agent installation¶
To verify S/MIME Transport Agent status, you can open Exchange Management Shell and input:
Get-TransportAgent
press enter
Check if there is EA Smime Agent installed and enabled in output.
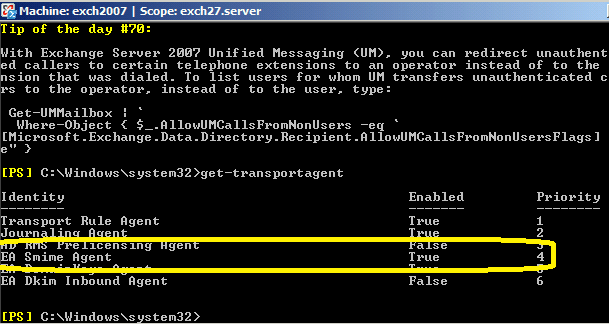
If there is no EA Smime Agent found, you can re-run installer directly
(do not uninstall) to fix this issue.
You can also contact support@emailarchitect.net for assistance.
Appendix: Email encryption and email disclaimer¶
Free Email Support¶
Not enough? Please contact our technical support team.
Remarks
We usually reply emails within 24hours. The reason for getting no response is likely that your SMTP server bounced our reply. In this case, please try to use another email address to contact us. Your Gmail, Hotmail or Office 365 email account is recommended.
