EmailArchitect Email Server supports multiple domains. The maximum number of domain it can support is restricted by the license agreement.
To configure domain settings, you have to logon as "system" user. Then click "Domains".
EmailArchitect Email Server supports 2 types of domain settings:
Local Domain
All users' settings and emails are stored in current local machine.
Only "system" user has the right to edit above options; domain administrator can only read these options.
Remote Domain
There is no user account in remote domain, all email sent to this domain will be forwarded to a local domain, email address or a remote host if forwarding function is activated.
Recipients Control in Remote Domain
For most email servers, every email to the remote domain will be accepted no matter the recipient is. For example, there is a remote domain named "testdomain" in the server, it will forward all email to (*@testdomain) this domain to another remote server, even the user doesn't exist on the remote server. That will consume a lot of networking resource. In the contrast, the administrator can set the valid recipients list in remote domain of EmailArchitect Email Server, any email to invalid recipients of remote domain will be rejected by EmailArchitect SMTP Service directly.
Delete Domain
Caution: Once a domain is deleted, all configuration files and user folders can't be restored. If you just want to disable current domain temporarily, you can uncheck "Active" in domain setting.
Default Domain
when the user logon to SMTP/POP3/IMAP4 service, the user need to use his email address(user@domain)
as the user name.
E.g.
myemail@mydomain.com
But if the domain is set to default domain, then the user can logon SMTP/POP3/IMAP4
service without domain.
E.g.
just use myemail as the username to logon SMTP/POP3/IMAP4 service is ok.
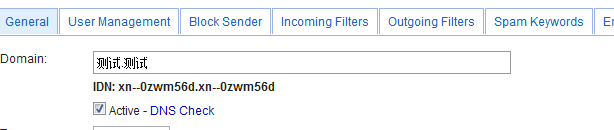
Internationalized Domain Name (IDN)
An internationalized domain name (IDN) is an Internet domain name that contains at least one label that is displayed in software applications, in whole or in part, in a language-specific script or alphabet, such as Arabic, Chinese, Russian, Tamil or the Latin alphabet-based characters with diacritics, such as French. These writing systems are encoded by computers in multi-byte Unicode. Internationalized domain names are stored in the Domain Name System as ASCII strings using Punycode transcription.
To create unicode domain in EmailArchitect server, you can simply input your domain name in "Create Domain". After you created domain, you can see IDN: your domain Punycode in Domain General Setting.

When you configure DNS setting, please make sure use the PunyCode domain but not your unicode domain.
See Also
Quick Tutorial User Permissions Domain Administration User Administration Services Administration SMTP Service POP3 Service IMAP4 Service Remote Object Call Service Webmail Service SSL Configuration Realtime Black List Anti-Spam Anti-Virus List Administration Traffic Control DBConnector Mail Archive DomainKeys and DKIM signature Storage and User Mailbox Incoming/outgoing Filters Advanced Functions in Filter Templates
EmailArchitect Server
Website
EmailArchitect Server Community
Logon As system user, create a local domain named "adminsystem.com". Create a user named "admin" in this domain and set this account as domain administrator. Set Max Users to 20, Quota Size to 100M and Catch-Al Alias to "admin@adminsystem.com" in domain setting.
Staff of Company A can use this account admin@adminsystem.com to logon Web Access and create other user accounts.